Bed Bugs: Behavior and Habits
Bedbugs– what are they? Bed bugs are tiny insects that can sneak into our homes and cause much trouble. But where do these pesky bugs come from? Well, bed bugs are good at hitching a ride. They can travel in clothes, suitcases, and even furniture.
Where are these bed bugs from? They may have come from many places. Maybe you stayed in a hotel with bed bugs, and they hitched a ride home with you. You got bedbugs from secondhand furniture.
However, eliminating bed bugs as quickly as possible is crucial. They’re small but can cause many issues if you ignore them.

Understanding Their Feeding Habits
What Bed Bugs Do When They Feed
- Bed bugs use their sharp mouthparts to pierce the skin of animals and humans.
- They inject saliva with anesthetics and anticoagulants to numb and prevent blood clotting.
- Bed bugs feed on blood for several minutes until they feel complete.
- After feeding, they return to their hiding place, where they will digest the blood meal and molt into their next life stage.
When Bed Bugs Feed
- Bed bugs usually feed at night when their hosts are asleep.
- Warmth and carbon dioxide from sleeping animals and humans attract them.
- Bed bugs can also feed during the day if they are hungry and their hosts are still.
- They can go without feeding for weeks or months but will provide when they sense their host is nearby.
How Bed Bug Bites Feel
- Bed bug bites can cause red, itchy welts on the skin.
- As bed bugs move along the skin while feeding, they often appear in lines or groups.
- Some people’s condition does not react to bed bug bites, while others have severe allergic reactions.
- Bed bug bites can cause discomfort but don’t spread diseases.

How Do Bed Bugs Make More Bed Bugs?
Courtship Behavior of Bed Bugs
- Before mating, bed bugs engage in courtship behavior, which involves the male tapping the female with his antennae and forelegs to assess her readiness to mate.
- The male also releases a pheromone (a chemical signal) that attracts the female and signals his intent to breed.
- Once the male has determined that the female is receptive to mating, he will mount her from behind and begin the traumatic insemination process.
Mating Habits of Bed Bugs
- Bed bugs reproduce by a process called “traumatic insemination,” which means that the male pierces the female’s abdomen with his reproductive organ and injects sperm directly into her body cavity.
- After mating, the female lays eggs in small cracks and crevices near their food source (human or animal blood).
- Bed bugs can produce over 200 offspring in their lifetime, with an average of 5 eggs per day.

Why do bed bugs mate this way?
Traumatic insemination may seem cruel and unusual to breed, but it’s a survival strategy for bed bugs. Bed bugs, parasites that feed on blood, are adept at hiding in cracks and crevices. Traumatic insemination lets bed bugs mate quickly without courtship rituals or predators.
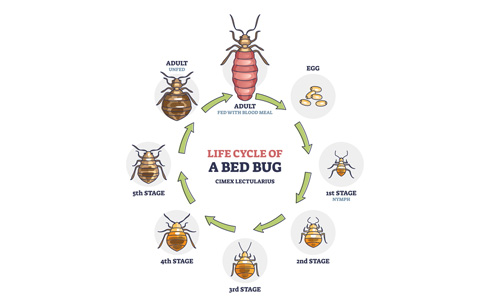
The Transformation of a Bed Bug
The First Stage of a Bed Bug’s Life
- Female bed bugs lay tiny white eggs about 1mm in size.
- Bed bugs glue 10–50 eggs to surfaces near blood sources.
- It takes about 6 to 10 days for the eggs to go through embryonic development when the baby bed bug grows inside the egg.
- The nymph hatches after developing inside the egg.
- The newborn larvae are the size of pinheads and are white or translucent when they first hatch.
What are bed bug nymphs?
Bed bug nymphs are baby bed bugs that hatch from eggs laid by adult female bed bugs. They’re 1/16 to 1/4 inch smaller than adult bed bugs. They are also lighter in color, often translucent or whitish-yellow.
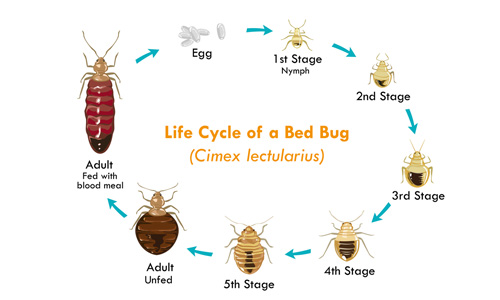
Nymph Development Stages
Bed bugs go through five nymph stages before reaching adulthood. The nymph’s development:
- First instar nymph: When bed bug eggs hatch, they release a larva that is about 1.5 millimeters in length. This first instar nymph is translucent and very small. It will molt or shed its exoskeleton to grow.
- Second instar nymph: After the first molt, the larva becomes a second instar nymph. At this stage, it is slightly larger and more visible. It will continue to feed on blood meals to grow and molt again.
- Third instar nymph: The larva is even more prominent at the third instar, and its color becomes darker. It has more distinct body segments, and its exoskeleton is thicker. It will molt again to continue growing.
- Fourth instar nymph: By the fourth instar, the larva is much closer in size and appearance to an adult bed bug. It looks like a sesame seed in size and color. It will molt one last time before becoming an adult.
- Fifth instar nymph: The fifth and final instar nymph looks almost identical to an adult bed bug. It is the later stage before becoming a fully mature adult. Once it has molted for the final time, it can reproduce and lay eggs.
How long do bed bug nymphs grow?
Temperature, humidity, and blood availability affect how long a bed bug nymph takes to become an adult. Under optimal conditions, a bed bug can take as little as five weeks to go from egg to adult. However, bed bugs can develop in less favorable conditions for several months or even a year.

The Final Countdown: How Long Do Bed Bugs Live?
Adult bed bugs are the final stage in the bed bug life cycle. They are the bed bug family’s most notorious bloodsuckers. Their lifespan is as follows:
- Depending on their environment, adult bed bugs can live for months or years. Generally, they tend to live longer in chillier climates with access to regular meals.
- Adult bed bugs will mate and lay eggs during their lifespan, contributing to the next generation of bed bugs.
- Bed bugs can live for months without eating but need blood to reproduce.
- While adult bed bugs can technically live for up to a year, they are vulnerable to some factors that can shorten their lifespan. Extreme temperatures, lack of food, and chemical treatments are all potential threats to the survival of adult bed bugs.

Don’t Let Bed Bugs Suck the Life Out of You.
Bed bugs may be tiny, but they can cause significant problems! These little bloodsuckers may intrigue you with their sneaky feeding and strange mating rituals. However, bed bugs can be a nuisance and a health risk.
Fortunately, you can eliminate bed bugs. Don’t panic if you suspect bed bugs. Contact a professional exterminator for bed bug heat treatment in San Francisco, CA to help. You can rest easy knowing these experts can identify, locate, and eliminate bed bugs.
Bed bugs may be tiny, but they can cause big headaches. You can better protect yourself from their bites and infestations by understanding their behavior and habits. And if bed bugs become a problem, remember that help is available from professional extermination services like the bed bug killer in San Francisco, CA. So, stay vigilant, stay informed, and sleep tight!







